15.09.2023
Explore the interactive Cool Up map
Discover the world of Cool Up by exploring the interactive Cool Up map. Click through the map to learn more about the Cool Up programme and to explore the world of sustainable cooling and natural refrigerants.
Jordan has shown sustained commitment to the Montreal Protocol by reducing the consumption of ozone-depleting substances (ODS) through different policies and strategies. Now, while Jordan implements the Kigali Amendment, the Cool Up programme is working to reduce cooling demand in the refrigeration and air conditioning sectors and introduce energy efficient technologies using natural refrigerants. This work will support the Government of Jordan in achieving its Kigali Amendment targets.
Egypt has shown sustained commitment to the Montreal Protocol by reducing the consumption of ozone-depleting substances through different policies and strategies. As Egypt ratified the Kigali Amendment, Cool Up is working with the Egyptian Ministry for the Environment as a political partner to create catalytic change in the refrigeration and air conditioning sector and ultimately upscale the deployment of sustainable cooling technologies in the Egyptian market.
Lebanon is a signatory of the Montreal Protocol and has ratified the Kigali Amendment. Lebanon has also developed a National Cooling Plan, which outlines a roadmap for the transition to carbon neutrality in the cooling sector by 2050, amongst other actions. Cool Up supports Lebanon in implementing the Kigali Amendment by developing relevant policies, developing technology and financial research and products, and deploying capacity building programmes.
Türkiye is a signatory of the Montreal Protocol and ratified the Kigali Amendment. Türkiye has had success in implementing an HCFC phase-out plan as well as strategies to reduce energy demand and increase energy efficiency. These successes indicate that there is now capacity to address HFC phase-down. Cool Up supports Türkiye in this work via, for example, building capacity and engaging with finance, industry, and policy stakeholders.
The Cool Up programme is part of the International Climate Initiative (IKI). The Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation, Nuclear Safety and Consumer Protection (BMUV) supports this initiative on the basis of a decision adopted by the German Bundestag.
The Cool Up programme brings together ten international, regional and national expert organisations. With in-depth expertise on topics like ozone depleting substances, natural refrigerants, f-gas regulation, energy efficiency, buildings, and climate, our team is well-equipped to support governments, industry, and financial institutions facilitate the transition to sustainable cooling.
Explore our session on Approaches to National Cooling Plans!
The Montreal Protocol is considered to be one of the most successful environmental agreements of all time and can serve as an inspirational example of what international cooperation can achieve.
The Kigali Amendment continues the Montreal Protocol’s historic legacy by phasing down the use of hydrofluorocarbons.
A longlist of technical solutions, which are proved to be relevant and mature solutions in many developed/developing countries, has been developed for each of the two main areas, air conditioning and commercial refrigeration. A systematic evaluation of the listed solutions has been done, resulting in recommendations for sustainable cooling solutions for the Cool Up partner countries.
The recommended solutions should face the lowest implementation barriers while simultaneously having high equivalent CO2 saving potentials without creating lock-in effects for the long-term aim of climate neutrality.
The suggested sustainable cooling solutions are in line with the Cool Up goals, which implies the absence of environmentally harmful refrigerants such as fluorinated gases, a low energy demand through high efficiency and compatibility with a fully renewable energy supply.
Natural refrigerants are non-synthetic, natural substances that are environmentally friendly, have very low or no global warming potential, and do not cause depletion of the ozone layer.
The transition to sustainable cooling requires financing for new equipment and changes in the manufacturing of refrigeration and air conditioning systems. Cool Up focuses on supporting financial institutes in leveraging existing financial models or developing new ones that can support the cooling market and improve access to finance for sustainable cooling technologies.
The programme builds on emerging sustainable banking sectors in Cool Up partner countries to incorporate sustainable cooling solutions into the technology portfolios of national and/or regional banks’. Cool Up’s work will focus on integrating these technologies into existing financial products and supporting the financial sector to design financial products and credit lines for sustainable cooling technologies. Cool Up facilitates knowledge sharing and capacity building amongst international banks, multilateral financial institutions, regional development finance institutions, and associations of financial institutions.
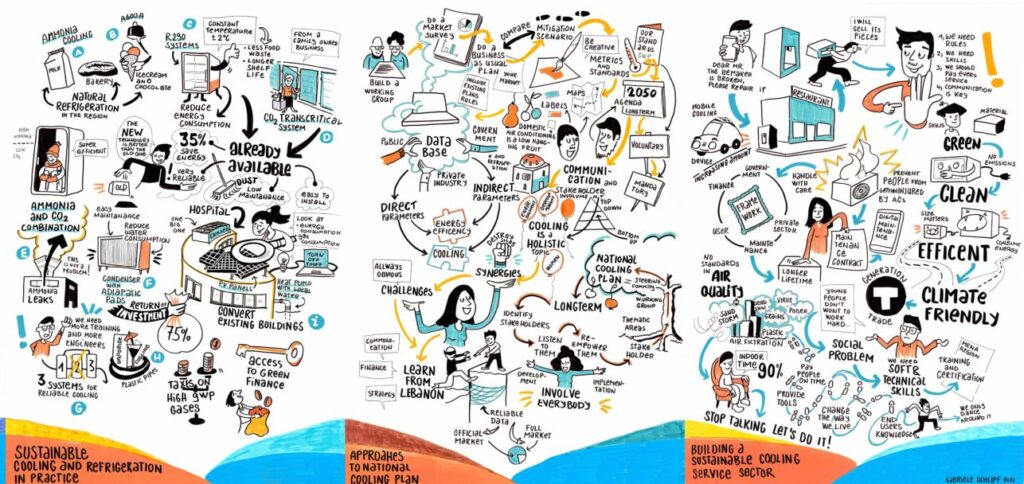
Explore our session on Sustainable cooling and refrigeration in practice.
Explore our session on Approaches to National Cooling Plan.
Explore our session on Building a sustainable service sector.
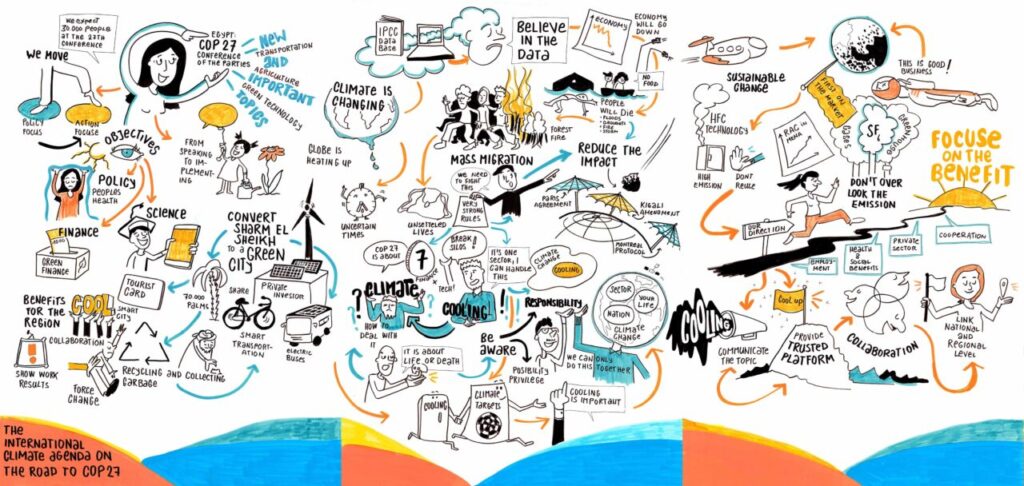
Explore our session on The international climate agenda on the road to COP27.
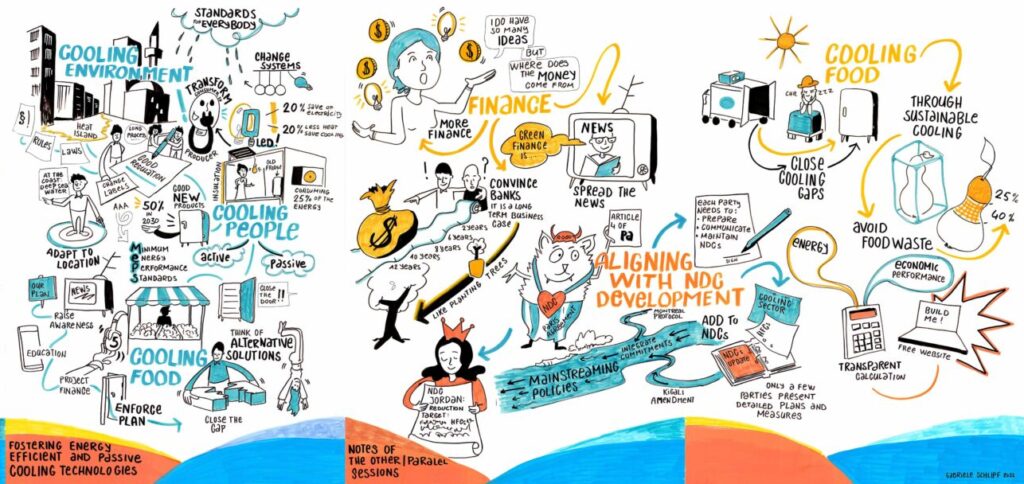
Explore our session on Fostering energy efficient and passive cooling technologies.
Explore our session on Notes of the other parallel sessions.
Natural refrigerants are non-synthetic, natural substances that are environmentally friendly, have very low or no global warming potential, and do not cause depletion of the ozone layer.
Commercial refrigeration contributes to climate change through direct refrigerant emissions and energy consumption, but is also vital to keep food fresh, especially in hot climates like the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. Natural refrigerants can help offset some of the negative effects of commercial cooling through more sustainable means. For a sector-wide transformation to occur, corporations will need to adopt and promote sustainable cooling and energy efficiency across the food supply chain.
As a part of the 2022 celebration of World Refrigeration Day, Cool Up hosted a webinar focusing on the benefits of using natural refrigerants for commercial refrigeration. The webinar drew on examples from the European Union and showcase the leading role of international trade and cooperation, specifically highlighting the global METRO F-gas exit programme in Türkiye and the use of natural refrigerants in a supermarket in Jordan. Join Cool Up as we look at ways to make commercial cooling better for people and the planet, across the MENA region and the globe.
A longlist of technical solutions, which are proved to be relevant and mature solutions in many developed/developing countries, has been developed for each of the two main areas, air conditioning and commercial refrigeration. A systematic evaluation of the listed solutions has been done, resulting in recommendations for sustainable cooling solutions for the Cool Up partner countries.
The recommended solutions should face the lowest implementation barriers while simultaneously having high equivalent CO2 saving potentials without creating lock-in effects for the long-term aim of climate neutrality.
The suggested sustainable cooling solutions are in line with the Cool Up goals, which implies the absence of environmentally harmful refrigerants such as fluorinated gases, a low energy demand through high efficiency and compatibility with a fully renewable energy supply.
Cool Up contributes to developing financial mechanisms and funding structures to boost the transition to a sustainable cooling market. Cool Up’s finance work builds on the success of the banking sectors efforts to substantiate renewable energy and energy efficiency investments by introducing sustainable cooling technologies as a new investment opportunity.
Skilled workforces will be needed to drive the upscaling of sustainable cooling practices. Learning new skills in shared, regional experiences helps to foster innovation in design and technologies, contributes to the widespread understanding of the economic benefits of sustainable cooling, and supports effective implementation of policies and regulations that contribute to national and international climate targets.
Cool Up’s theoretical and practical skills training brings together stakeholders in industry, policy, and finance from across our partner countries.
The Cooling Sector Status Report aims to rectify this on residential and non-residential air conditioning and commercial refrigeration. The report provides an overview of the cooling sector in Lebanon, Egypt, Jordan and Türkiye by laying the foundation for understanding upscaling sustainable cooling technologies potential in the country and the use of natural refrigerants as an alternative to harmful synthetic refrigerants.
The Cool Up prospects study aims at developing one current trend and three mitigation prospects with different alternatives for transition. Its objectives include creating:
- an understanding of possible sustainable development pathways for the air conditioning (AC) sector and the commercial refrigeration sector, as well as
- the basis for the development of policy and finance measures
The Montreal Protocol is considered to be one of the most successful environmental agreements of all time and can serve as an inspirational example of what international cooperation can achieve.
The Kigali Amendment continues the Montreal Protocol’s historic legacy by phasing down the use of hydrofluorocarbons.
Explore our session on Approaches to National Cooling Plans!
During the Cool Up regional conference in 2022, Cool Up organised a ‘Breakfast for Women in Sustainable Cooling’ gathering ambitious women working towards the sustainable cooling transition who participated the regional conference to talk about gender equality in the workplace. The breakfast was moderated by Cool Up’s national partner Eng. Sawsan Bawaresh from the Royal Scientific Society in Jordan, and gave female leaders working in sustainable cooling the opportunity to share their experiences and engage in this informal networking forum with like-minded colleagues.
The one-hour breakfast allowed for an open discussion about the role of women in the sustainable cooling transition by sharing success stories and advices, celebrating each other’s achievements, and motivating each other in a positive and intimate atmosphere.
The Cool Up programme brings together ten international, regional and national expert organisations. With in-depth expertise on topics like ozone depleting substances, natural refrigerants, f-gas regulation, energy efficiency, buildings, and climate, our team is well-equipped to support governments, industry, and financial institutions facilitate the transition to sustainable cooling.
The catalogue of technical solutions for sustainable cooling addresses stakeholders from different sectors, such as policy makers and financing bodies but it also addresses planners, manufacturers, and everyone who is interested.
The key intention is to facilitate the uptake of sustainable cooling in Lebanon with a specific focus on air conditioning and commercial refrigeration.
Policy and regulation are powerful stimuli to encourage the uptake of new technologies. In Cool Up we support our partner country governments in leveraging policies that can accelerate the implementation of the Kigali Amendment.
Cool Up is working closely with partner country governments to identify and implement recommendations to support the development, uptake, and awareness of sustainable cooling. Key areas for support include national governments’ ongoing work on international protocols and commitments, national plans and strategies, laws, bylaws, regulations, standards and codes. The goal of the policy and regulatory support is to provide technical assistance to each Cool Up partner country government on developing overarching national strategies such as national cooling action plans or roadmaps.
Thematic group meetings have brought together relevant stakeholders and decision makers in the industry and finance space in Türkiye, Jordan and Lebanon.
These meetings captured the perspective of the industry and finance sectors and identified their needs, risks, challenges and best practices for the deployment of sustainable cooling technology investments in the financial services industry.
Skilled workforces will be needed to drive the upscaling of sustainable cooling practices. Learning new skills in shared, regional experiences helps to foster innovation in design and technologies, contributes to the widespread understanding of the economic benefits of sustainable cooling, and supports effective implementation of policies and regulations that contribute to national and international climate targets.
Cool Up’s theoretical and practical skills training brings together stakeholders in industry, policy, and finance from across our partner countries.
COP 27 took place in Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt in 2022. This is particularly exciting as it drew attention to sustainability and climate efforts and initiatives in the MENA region.
The Cool Up team had a highly experienced team at COP covering climate, finance, and cooling expertise to help accelerate action towards sustainable cooling and beyond. Our focus is to stay closely linked to the national targets, strategies, plans, and programmes in partner countries.
The Cool Up programme organised and further participated in several events. We addressed the necessary market and paradigm shift to upscale solutions for sustainable cooling and provide an overview of sustainable cooling applications employing natural refrigerants and their role in reducing the overall electricity demand and reducing environmental impacts. The importance of national cooling plans in the countries under discussion were addressed, including high sector-specific ambition and financing models for transitioning to sustainable cooling technologies.
Explore our session on Sustainable cooling and refrigeration in practice
Policy and regulation are powerful stimuli to encourage the uptake of new technologies. In Cool Up we support our partner country governments in leveraging policies that can accelerate the implementation of the Kigali Amendment.
Cool Up is working closely with partner country governments to identify and implement recommendations to support the development, uptake, and awareness of sustainable cooling. Key areas for support include national governments’ ongoing work on international protocols and commitments, national plans and strategies, laws, bylaws, regulations, standards and codes. The goal of the policy and regulatory support is to provide technical assistance to each Cool Up partner country government on developing overarching national strategies such as national cooling action plans or roadmaps.
The transition to sustainable cooling requires financing for new equipment and changes in the manufacturing of refrigeration and air conditioning systems. Cool Up focuses on supporting financial institutes in leveraging existing financial models or developing new ones that can support the cooling market and improve access to finance for sustainable cooling technologies.
The programme builds on emerging sustainable banking sectors in Cool Up partner countries to incorporate sustainable cooling solutions into the technology portfolios of national and/or regional banks’. Cool Up’s work will focus on integrating these technologies into existing financial products and supporting the financial sector to design financial products and credit lines for sustainable cooling technologies. Cool Up facilitates knowledge sharing and capacity building amongst international banks, multilateral financial institutions, regional development finance institutions, and associations of financial institutions.
The Montreal Protocol is considered to be one of the most successful environmental agreements of all time and can serve as an inspirational example of what international cooperation can achieve.
The Kigali Amendment continues the Montreal Protocol’s historic legacy by phasing down the use of hydrofluorocarbons.
The Cool Up programme brings together ten international, regional and national expert organisations. With in-depth expertise on topics like ozone depleting substances, natural refrigerants, f-gas regulation, energy efficiency, buildings, and climate, our team is well-equipped to support governments, industry, and financial institutions facilitate the transition to sustainable cooling.
A longlist of technical solutions, which are proved to be relevant and mature solutions in many developed/developing countries, has been developed for each of the two main areas, air conditioning and commercial refrigeration. A systematic evaluation of the listed solutions has been done, resulting in recommendations for sustainable cooling solutions for the Cool Up partner countries.
The recommended solutions should face the lowest implementation barriers while simultaneously having high equivalent CO2 saving potentials without creating lock-in effects for the long-term aim of climate neutrality.
Follow Cool Up on LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/cool-up-programme/
Follow Cool Up on Twitter: https://twitter.com/WeAreCoolUp
Explore Cool Up’s website: https://www.coolupprogramme.org/
Sign up for Cool Up’s newsletter: https://www.coolupprogramme.org/contact/
The Cool Up programme held its inaugural regional conference, ‘Realising Opportunities for Sustainable Cooling,’ between 28-29 September 2022 in Istanbul, Türkiye. The conference provided an opportunity to bring together actors and stakeholders from the technical, policy, and finance communities across the Cool Up partner countries—Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, and Türkiye—for a regional exchange on the uptake of sustainable cooling and natural refrigerants.
Policy and regulation are powerful stimuli to encourage the uptake of new technologies. In Cool Up we support our partner country governments in leveraging policies that can accelerate the implementation of the Kigali Amendment.
Cool Up is working closely with partner country governments to identify and implement recommendations to support the development, uptake, and awareness of sustainable cooling. Key areas for support include national governments’ ongoing work on international protocols and commitments, national plans and strategies, laws, bylaws, regulations, standards and codes. The goal of the policy and regulatory support is to provide technical assistance to each Cool Up partner country government on developing overarching national strategies such as national cooling action plans or roadmaps.
Skilled workforces will be needed to drive the upscaling of sustainable cooling practices. Learning new skills in shared, regional experiences helps to foster innovation in design and technologies, contributes to the widespread understanding of the economic benefits of sustainable cooling, and supports effective implementation of policies and regulations that contribute to national and international climate targets.
Cool Up’s theoretical and practical skills training brings together stakeholders in industry, policy, and finance from across our partner countries.
Cool Up contributes to developing financial mechanisms and funding structures to boost the transition to a sustainable cooling market. Cool Up’s finance work builds on the success of the banking sectors efforts to substantiate renewable energy and energy efficiency investments by introducing sustainable cooling technologies as a new investment opportunity.
Cool Up’s MENA Region Cooling Status Report is the first of its kind to provide an overview of the state of sustainable cooling in the region. The report closes knowledge gaps by addressing progress, opportunities, and insights on the topic from the perspectives of policy, technology, markets, and finance.
A longlist of technical solutions, which are proved to be relevant and mature solutions in many developed/developing countries, has been developed for each of the two main areas, air conditioning and commercial refrigeration. A systematic evaluation of the listed solutions has been done, resulting in recommendations for sustainable cooling solutions for the Cool Up partner countries.
The recommended solutions should face the lowest implementation barriers while simultaneously having high equivalent CO2 saving potentials without creating lock-in effects for the long-term aim of climate neutrality.
The suggested sustainable cooling solutions are in line with the Cool Up goals, which implies the absence of environmentally harmful refrigerants such as fluorinated gases, a low energy demand through high efficiency and compatibility with a fully renewable energy supply
Commercial refrigeration contributes to climate change through direct refrigerant emissions and energy consumption, but is also vital to keep food fresh, especially in hot climates like the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. Natural refrigerants can help offset some of the negative effects of commercial cooling through more sustainable means. For a sector-wide transformation to occur, corporations will need to adopt and promote sustainable cooling and energy efficiency across the food supply chain.
As a part of the 2022 celebration of World Refrigeration Day, Cool Up hosted a webinar focusing on the benefits of using natural refrigerants for commercial refrigeration. The webinar drew on examples from the European Union and showcase the leading role of international trade and cooperation, specifically highlighting the global METRO F-gas exit programme in Türkiye and the use of natural refrigerants in a supermarket in Jordan. Join Cool Up as we look at ways to make commercial cooling better for people and the planet, across the MENA region and the globe.
Cool Up contributes to developing financial mechanisms and funding structures to boost the transition to a sustainable cooling market. Cool Up’s finance work builds on the success of the banking sectors efforts to substantiate renewable energy and energy efficiency investments by introducing sustainable cooling technologies as a new investment opportunity.
Explore our session on Fostering energy efficient and passive cooling technologies.
The transition to sustainable cooling requires financing for new equipment and changes in the manufacturing of refrigeration and air conditioning systems. Cool Up focuses on supporting financial institutes in leveraging existing financial models or developing new ones that can support the cooling market and improve access to finance for sustainable cooling technologies.
The programme builds on emerging sustainable banking sectors in Cool Up partner countries to incorporate sustainable cooling solutions into the technology portfolios of national and/or regional banks’. Cool Up’s work will focus on integrating these technologies into existing financial products and supporting the financial sector to design financial products and credit lines for sustainable cooling technologies. Cool Up facilitates knowledge sharing and capacity building amongst international banks, multilateral financial institutions, regional development finance institutions, and associations of financial institutions.
Explore our session on The international climate agenda on the road to COP27.
Commercial refrigeration contributes to climate change through direct refrigerant emissions and energy consumption, but is also vital to keep food fresh, especially in hot climates like the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. Natural refrigerants can help offset some of the negative effects of commercial cooling through more sustainable means. For a sector-wide transformation to occur, corporations will need to adopt and promote sustainable cooling and energy efficiency across the food supply chain.
As a part of the 2022 celebration of World Refrigeration Day, Cool Up hosted a webinar focusing on the benefits of using natural refrigerants for commercial refrigeration. The webinar drew on examples from the European Union and showcase the leading role of international trade and cooperation, specifically highlighting the global METRO F-gas exit programme in Türkiye and the use of natural refrigerants in a supermarket in Jordan. Join Cool Up as we look at ways to make commercial cooling better for people and the planet, across the MENA region and the globe.
Explore our session on Sustainable cooling and refrigeration in practice
Explore our session on Building a sustainable service sector
Explore our session on Approaches to National Cooling Plans
Explore our session on Notes of the other parallel sessions